
23 May 2025
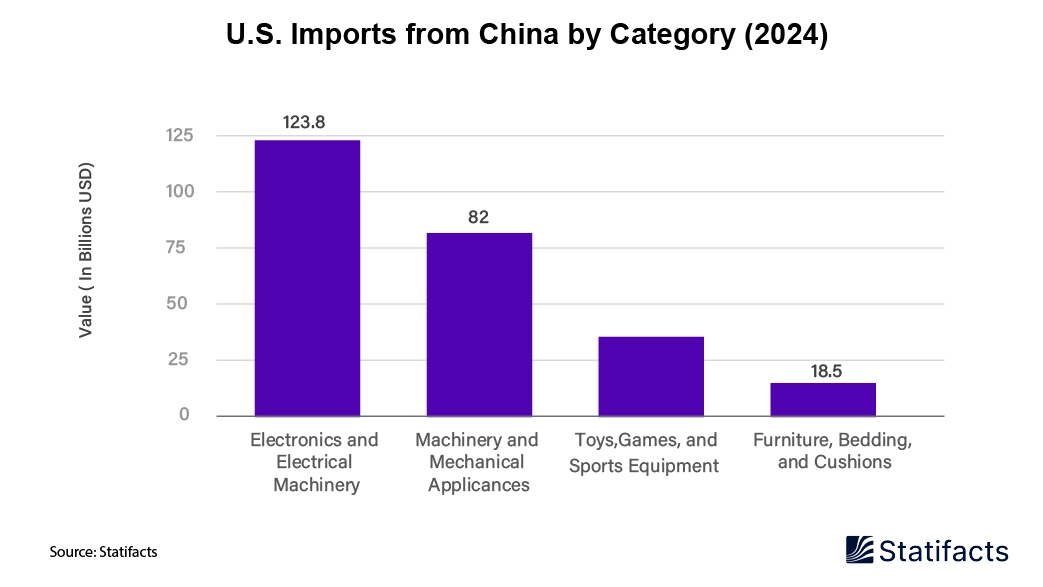
A possible intensification of the U.S.-China trade war could completely remake the American consumer goods landscape. Industry experts predict price hikes across the board, supply chain instability, and radical changes in buying habits that could profoundly affect household wallets and retailer strategies. As policymakers grapple over tariff levels and trade barriers, consumer goods firms are racing to prepare for possibilities that could impact everything from smartphones and clothing to household appliances and toys. The United States imported around $462.62 billion of goods from China in 2024. Electronics and electrical machinery were the largest import segment, with a total value of about $123.8 billion. It was followed by $82 billion worth of machinery and mechanical appliances. Toys, games, and sporting goods were worth $30 billion, and there were about $18.5 billion worth of furniture, bedding, and cushions. These are the high amounts of goods related to consumers imported from China, highlighting China's prominence in providing necessary commodities to the United States market.
"The consumer goods sector represents the most visible and immediate impact of any trade war escalation," said Dr. Maria Gonzalez, Senior Economist at the Consumer Goods Research Institute, commenting on the U.S.-China trade war. "Unlike industrial commodities, these are products that directly touch American families' daily lives, from the smartphones they use to the clothes they wear and the appliances in their homes."
With smartphones, laptops, gaming consoles, and home entertainment systems all relying on substantial Chinese manufacturing, electronics will be the most exposed. Apple sources approximately 70% of the components for each iPhone from Chinese suppliers, while Dell and HP source 85% for laptops from China. Industry estimates indicate that a 25% tariff would raise retail prices of smartphones by an average of $150-$300; the expected reaction from the consumer would be to further reduce spending on smartphones by 15-20%.
The clothing and textile industry faces similarly large challenges. Major retailers such as Walmart, Target, and Amazon send approximately 60% of their clothing purchases to Chinese manufacturers. A U.S.-China trade war may require these companies to swiftly diversify their supplier chains to countries such as Vietnam, Bangladesh, and Mexico, potentially raising clothing prices 20-35% short term.
Consumer consumption patterns from prior trade disputes offer clues on the possible impacts. When the United States entered trade disputes with other countries between 2018-2020, American consumers exhibited different price sensitivities depending on product categories. The demand for important electronics held steady after price increases; however, demand for discretionary items, such as luxury goods and some non-essential home products, diminished significantly.
E-commerce platforms encounter their challenges, especially companies like Amazon, which is highly dependent on Chinese suppliers to meet marketplace inventories. Small and medium-sized sellers that work with Chinese manufacturers for private-label products will likely feel margin pressure that will cause consolidation in the marketplace.
As companies look for solutions to avoid market disruption, innovations in supply chain technologies are moving along at breakneck speed. Utilisation of advanced analytics, AI-powered sourcing platforms, and blockchain-enabled supply chain tracking systems is becoming essential for ongoing operational flexibility and redundancy in the supply chain. When companies begin looking at and investing in "nearshoring" strategies, they create facilities that are in much closer proximity to U.S. markets and lessen their reliance on transcontinental supply chains.
Research into consumer behaviour identifies considerable demographic differences regarding trade war implications. Young consumers feel willing to pay higher prices for products they perceive as better quality or produced ethically, with the price-sensitive segments anticipating both substitution behaviours when switching towards lower cost alternatives.
Long-term effects extend beyond impacts on price alone. A protracted trade would have the potential to accelerate the "Made in USA" movement, possibly re-establishing local manufacturing in certain types of consumer goods. It will take both time and money to grow back domestic production capability, so any consumer impacts in the short term would be expected to be considerable.
Regional differences in the United States will likely take precedence. Retail sectors of states with greater import dependency (e.g., California, New York, and Florida) would be expected to see quicker consumer impacts in regard to the U.S.-China trade war, with more opportunities perhaps emerging in regions with greater local manufacturing metrics, assuming greater production demand local-regionally.
There are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form
URL TO BE USED AS REFERENCE LINK:
Placeholder content for this accordion, which is intended to demonstrate the .accordion-flush class. This is the first item's
accordion body.
Placeholder content for this accordion, which is intended to demonstrate the .accordion-flush class. This is the second item's
accordion body. Let's imagine this being filled with some actual content.
Placeholder content for this accordion, which is intended to demonstrate the .accordion-flush class. This is the third
item's accordion body. Nothing more exciting happening here in terms of content, but just filling up the space to make it look, at least at
first glance, a bit more representative of how this would look in a real-world application.
Do you still any question?
Feel free to contact us anytime using our contact form or visit our FAQ page.
Your contact to the Infographics Newsroom
