By clicking “Accept All Cookies” you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Privacy Policy
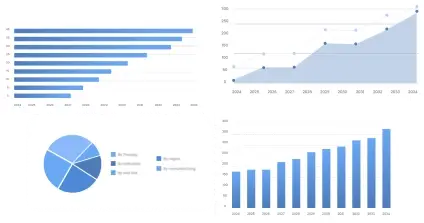
The global nucleic acid methylation market size was estimated at USD 3,450 million in 2024 and is projected to be worth around USD 13,660 million by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 14.75% from 2025 to 2034.
| Industry Worth | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 3,960 Million |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 13,660 Million |
| Market Growth Rate from 2025 to 2034 | CAGR of 14.75% |
The nucleic acid methylation market refers to the production, distribution, and application of nucleic acid methylation, which is a chemical modification of DNA and other molecules that may be retained as cells divide to make more cells. In DNA, methylation can alter gene expression. Methylation is a chemical reaction in the body in which a small molecule called a methyl group gets added to DNA, proteins, or other molecules. Nucleic acid methylation, particularly DNA methylation, plays an important role in silencing retroviral elements, regulating tissue-specific gene expression, genomic imprinting, and X chromosome inactivation. Methylation is a first-line essential biochemical process in the transmission of life, playing an important role in the modification of DNA and histones. It is involved in regulating gametogenesis, embryonic and placental growth as well as imprinting and epigenesis.
DNA methylation is important for normal development, and it plays an important role in several key processes, including genomic imprinting, X-chromosome inactivation, and suppression of repetitive element transcription and transposition, and when dysregulated, contributes to diseases like cancer. Epigenetic patterns like DNA methylation act as important regulatory roles in DNA-based processes, including transcription, replication, and DNA repair. DNA methylation acts as a conduit between gene expression and important regulatory mechanisms that govern genome integrity.
Increasing investment in precision medicine is driving the growth of the nucleic acid methylation market. Advances in precision medicine manifest into tangible benefits such as early detection of disease and designing personalized treatments are becoming more commonplace in healthcare. The power of precision medicine to personalize care is allowed by several data collection and analytics technologies. The ability of our healthcare provider to use genetic information as part of routine medical care. A better understanding of why diseases occur.
The capability to predict which treatments will work best. Precision medicine is emerging at its pace, and slow and steady progress is seen on many fronts, such as genomics, big data, biobanks, lifestyle monitoring, health information infrastructure, reimbursement, and policy. In future decades, precision medicine will lead to growth and adoption. Due to advances in precision medicine, doctors can customize a clinical approach to a patient’s ailment or disease based on factors like genetics, lifestyle, and environment.
Rising use of methylation markers for early disease detection driving the growth of the nucleic acid methylation market. Alterations in DNA methylation patterns in the genome have been observed across malignancies and usually occur before other detectable genetic changes. Therefore, biomarker mining for the early diagnosis of cancer based on DNA methylation has emerged as a promising field and has become a focus of research globally.
Additionally, to identify modifiable risk factors and supplement deficiencies, genetic testing can also reveal insights into methylation genes. Methylation is a process that occurs in our bodies and is responsible for turning genes on and off. Methylation within the promoter regions of tumor suppression genes causes their silencing, and methylation within the gene itself can induce mutational events. These mechanisms can play a fundamental role in precipitating the development of a large and diverse number of human cancers.
Published by Ajit Bansod
| Subsegment | 2024 | 2025 | 2026 | 2027 | 2028 | 2029 | 2030 | 2031 | 2032 | 2033 | 2034 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kits & Reagents | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Enzymes | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Services | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Instruments & Software | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Consumables | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Subsegment | 2024 | 2025 | 2026 | 2027 | 2028 | 2029 | 2030 | 2031 | 2032 | 2033 | 2034 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DNA Methylation | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| RNA Methylation | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Subsegment | 2024 | 2025 | 2026 | 2027 | 2028 | 2029 | 2030 | 2031 | 2032 | 2033 | 2034 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Bisulfite Sequencing & PCR-based Techniques | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Microarray-based Methylation Analysis | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Mass Spectrometry | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Hybridization-based & Antibody-based Detection | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Subsegment | 2024 | 2025 | 2026 | 2027 | 2028 | 2029 | 2030 | 2031 | 2032 | 2033 | 2034 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug Discovery & Personalized Medicines | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Clinical Diagnostics | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Others | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Subsegment | 2024 | 2025 | 2026 | 2027 | 2028 | 2029 | 2030 | 2031 | 2032 | 2033 | 2034 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceutical & Biotechnology Companies | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Academic & Research Institutes | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Hospitals & Diagnostic Laboratories | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
To get full access to our Market Insights, you need a Professional Account or a Business Suite.

You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.

You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.

Our customers work more efficiently and benefit from