By clicking “Accept All Cookies” you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Privacy Policy
Asia Pacific Fertility Market (By Offering: Assisted Reproductive Technology (IVF, Artificial Insemination, Surrogacy, Others), Fertility Drugs (Gonadotropin, Anti-estrogen, Others); By End User: Fertility Clinics, Hospitals, Clinical Research Institutes; By Region: North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa) Industry Size, Share, Growth, Trends 2025 to 2034
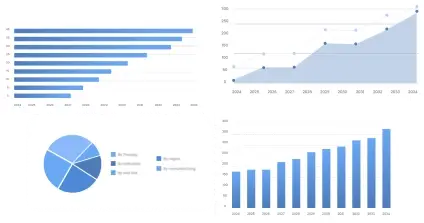
The asia pacific fertility market size was valued at USD 9.10 billion in 2024, is set to reach USD 25.65 billion by 2034, driven by rising infertility rates, expanding ART adoption, and growing investment in advanced reproductive care (CAGR 10.92%).
| Reports Attributes | Statistics |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 9.10 Billion |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 9.98 Billion |
| Market Size in 2031 | USD 18.49 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 25.65 Billion |
| CAGR 2025 to 2034 | 10.92% |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 to 2034 |
Demand in the Asia Pacific region is increasing due to demographic factors that influence fertility patterns. According to the World Health Organization (2023), infertility affects one in six individuals worldwide, and countries in Asia experience significant burdens linked to lifestyle shifts, environmental exposures, and rising maternal age. In large countries such as China and India, rapid urbanization and workforce pressure contribute to delayed marriages and childbirth, which heightens the need for fertility-related medical interventions. National health authorities in several Asia Pacific countries report that the average age at first childbirth has increased steadily over the past decade.
Growing awareness and normalization of fertility treatments are also driving demand. Public health campaigns in China, India, Japan, and Southeast Asian countries promote reproductive health screenings, and professional medical societies have expanded guidance on infertility management. Fertility preservation, including egg and sperm freezing, is gaining acceptance in urban centers, supported by educational efforts from national fertility associations. Digital technologies that enable early fertility assessment are increasingly used, further increasing demand for both diagnostic and treatment services.
Access and affordability are key challenges. In many countries across the Asia Pacific, fertility treatments are not uniformly covered by national insurance schemes, leading to significant out-of-pocket costs. Reports from regional health ministries have highlighted that the cost of in vitro fertilization can be prohibitive in lower and middle-income countries, reducing access for large segments of the population. Geographic disparities also limit growth. Urban centers tend to have advanced fertility clinics, while rural areas lack specialized reproductive medicine facilities, which restricts equitable access.
Cultural and regulatory factors present additional obstacles. In parts of the region, social stigma surrounding infertility or fertility treatments discourages individuals from seeking medical support. Some countries impose legal restrictions on gamete donation, surrogacy, or embryo storage, which affects clinic operations and patient choices. Workforce limitations, including a shortage of trained embryologists and reproductive endocrinologists, further constrain clinics' ability to expand capacity. Although AI and laboratory automation can support efficiency, adoption varies widely across the region due to policy differences and resource constraints.
Asia Pacific is highly diverse in terms of fertility infrastructure and policy frameworks. China and India represent the largest potential patient base due to their population sizes and rising infertility prevalence reported by national health authorities. These countries are seeing ongoing investment in fertility clinics, laboratory equipment, and digital health platforms that enable remote fertility assessments. Japan, South Korea, Singapore, and Australia have advanced reproductive medicine sectors supported by strong regulatory guidance and robust professional medical societies.
Several governments in the region have expanded fertility support programs to address declining birth rates. For example, national statistics offices in East Asia report historically low fertility rates, prompting health ministries to introduce subsidies, insurance coverage expansions, and public funding for assisted reproductive technologies. Southeast Asian countries are also increasing investment in reproductive health programs to meet growing demand. AI-assisted embryo imaging and machine learning models used in laboratory decision-making are gaining traction in advanced markets such as Japan and Australia.
China’s fertility market is shaped by shifting demographic policies and rising infertility prevalence. The National Health Commission has highlighted growing concern regarding declining birth rates, which has increased interest in fertility support programs. Public awareness campaigns and expanded access to reproductive health screening contribute to rising demand. Major cities such as Shanghai and Beijing host advanced ART centers that adopt digital lab systems and AI-enhanced embryo selection tools. However, affordability remains an issue, and access varies significantly between urban and rural areas.
India has a rapidly expanding fertility services landscape supported by a large population experiencing rising infertility. The Indian Council of Medical Research and the Ministry of Health report steady demand due to lifestyle changes, delayed marriages, and rising reproductive health challenges. Large urban centers such as Mumbai, Delhi, and Bengaluru have advanced ART facilities offering IVF, ICSI, and fertility preservation services. Public awareness campaigns have increased understanding of fertility health, while digital teleconsultation platforms are improving access. Access inequality persists at the rural level, where specialized clinics remain limited.
Japan faces one of the lowest fertility rates globally, which has intensified government attention on reproductive health support. The Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare has implemented subsidy programs to improve the affordability of assisted reproductive technologies. Japan’s clinical sector is technologically advanced, with strong adoption of AI-enabled embryo assessments and high-precision laboratory equipment. Public acceptance of fertility treatments has grown due to demographic pressure and national awareness campaigns. However, high treatment costs and long waiting times remain barriers for some patients.
| Segments | Shares (%) |
| Assisted Reproductive Technology | 7% |
| Fertility Drugs | 10% |
| Segments | Shares (%) |
| Fertility Clinics | 55% |
| Hospitals | 35% |
| Clinical Research Institutes | 10% |
Published by Ajit Bansod
| Offering | 2024 | 2025 | 2026 | 2027 | 2028 | 2029 | 2030 | 2031 | 2032 | 2033 | 2034 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Assisted Reproductive Technology | 6.37 | 7.05 | 7.79 | 8.62 | 9.53 | 10.54 | 11.66 | 12.90 | 14.26 | 15.77 | 17.44 |
| Fertility Drugs | 2.73 | 3.04 | 3.41 | 3.80 | 4.24 | 4.74 | 5.29 | 5.90 | 6.59 | 7.36 | 8.21 |
| End User | 2024 | 2025 | 2026 | 2027 | 2028 | 2029 | 2030 | 2031 | 2032 | 2033 | 2034 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fertility Clinics | 4.55 | 5.03 | 5.55 | 6.13 | 6.78 | 7.49 | 8.27 | 9.14 | 10.09 | 11.15 | 12.31 |
| Hospitals | 3.18 | 3.54 | 3.94 | 4.38 | 4.88 | 5.42 | 6.03 | 6.71 | 7.46 | 8.30 | 9.24 |
| Clinical Research Institutes | 1.37 | 1.52 | 1.71 | 1.91 | 2.11 | 2.37 | 2.65 | 2.95 | 3.30 | 3.68 | 4.10 |
| Subsegment | 2024 | 2025 | 2026 | 2027 | 2028 | 2029 | 2030 | 2031 | 2032 | 2033 | 2034 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Assisted Reproductive Technology | 6.37 | 7.05 | 7.79 | 8.62 | 9.53 | 10.54 | 11.66 | 12.90 | 14.26 | 15.77 | 17.44 |
| Fertility Drugs | 2.73 | 3.04 | 3.41 | 3.80 | 4.24 | 4.74 | 5.29 | 5.90 | 6.59 | 7.36 | 8.21 |
| Subsegment | 2024 | 2025 | 2026 | 2027 | 2028 | 2029 | 2030 | 2031 | 2032 | 2033 | 2034 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fertility Clinics | 4.55 | 5.03 | 5.55 | 6.13 | 6.78 | 7.49 | 8.27 | 9.14 | 10.09 | 11.15 | 12.31 |
| Hospitals | 3.18 | 3.54 | 3.94 | 4.38 | 4.88 | 5.42 | 6.03 | 6.71 | 7.46 | 8.30 | 9.24 |
| Clinical Research Institutes | 1.37 | 1.52 | 1.71 | 1.91 | 2.11 | 2.37 | 2.65 | 2.95 | 3.30 | 3.68 | 4.10 |
To get full access to our Market Insights, you need a Professional Account or a Business Suite.

You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.

You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.

Our customers work more efficiently and benefit from